- 10 Rue de l'ile de Rhodes, 3rd floor Office A1 Henda Building 1053 Lac 2 Tunis
- 2 Place de Paris 54500 Vandœuvre-lès-Nancy
- contact@anyinit.com
Any In IT We offer support for those looking to make their digital projects a reality. With our experience and total commitment, we are here to transform your ideas into concrete successes, with transparency and dedication.

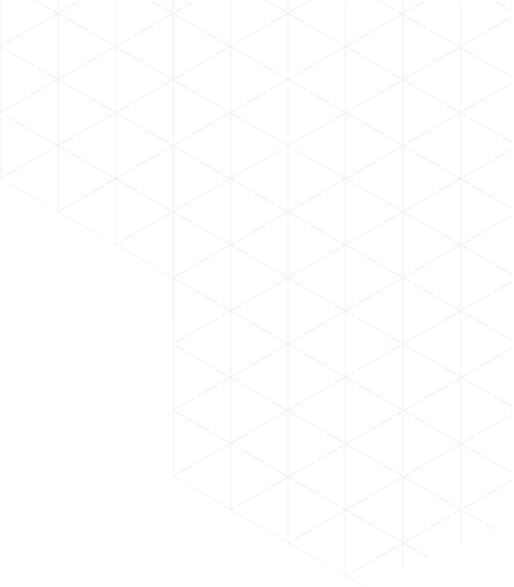


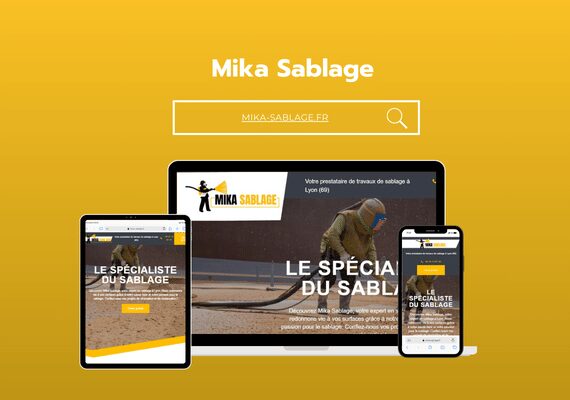


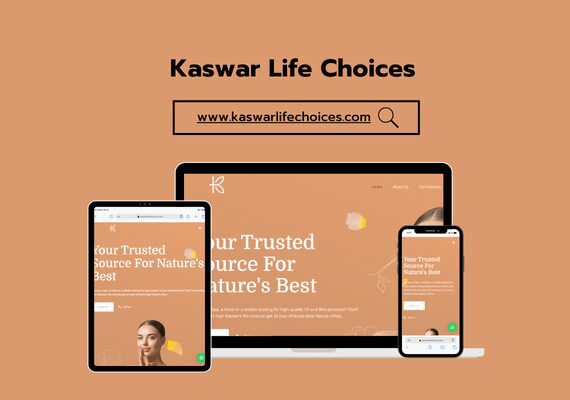
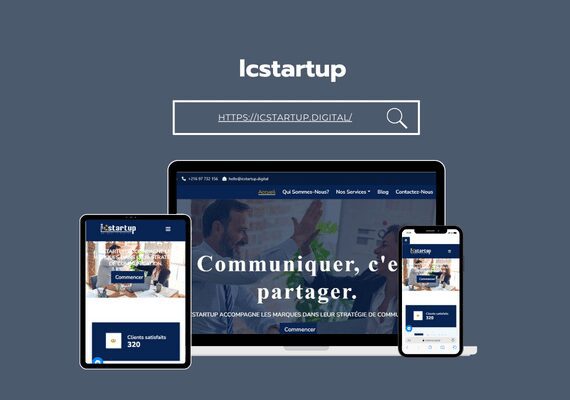



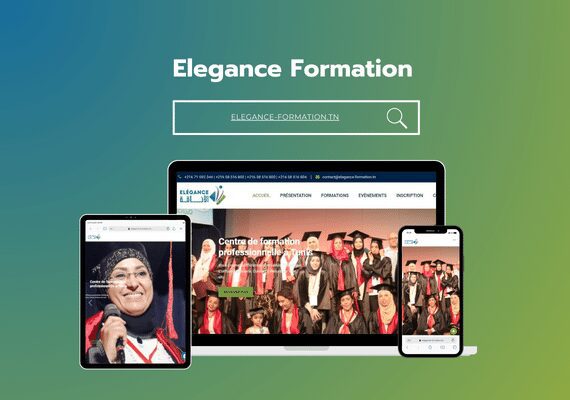
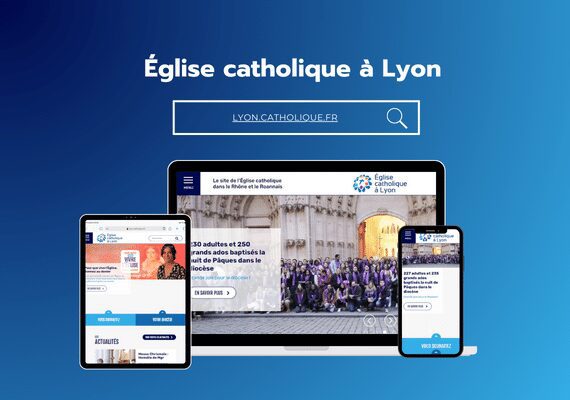
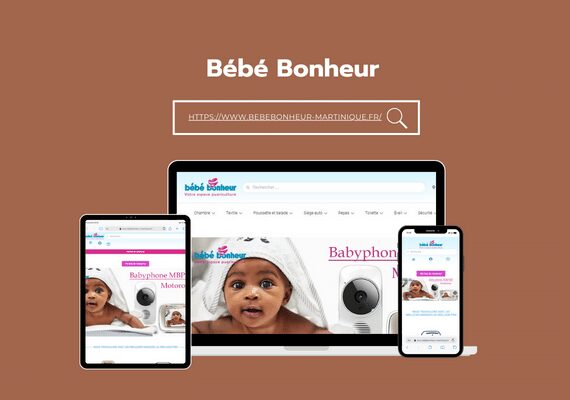
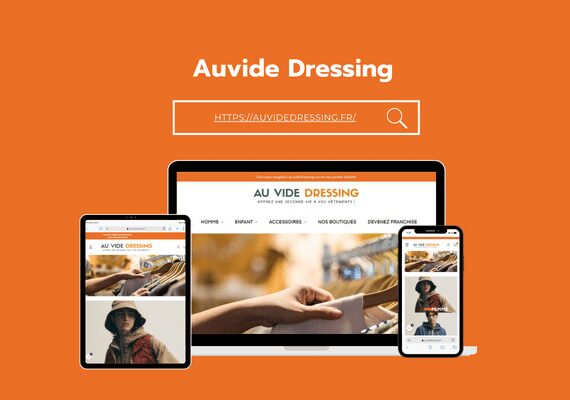
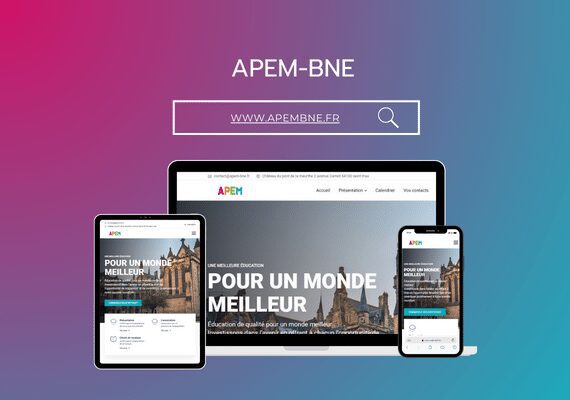
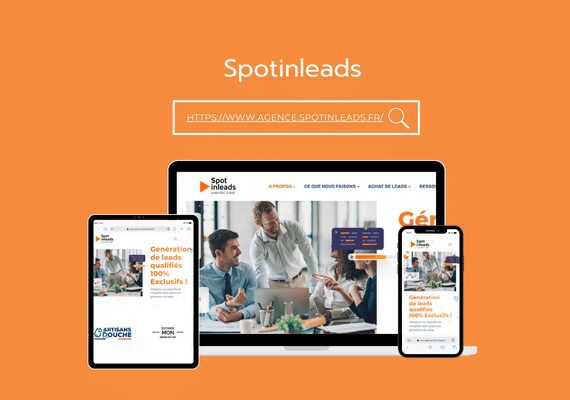




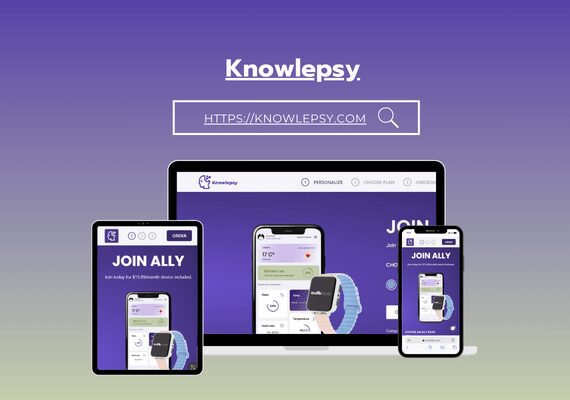


















































Mr. MAAROUFI is the best web developer in the world. As a lawyer, he created my website very professionally and was always available. I am very satisfied with his work and highly recommend him. Thank you so much, dear Mr. MAAROUFI.